Ⅰ. What is a collaborative robot?
“Collaboration” (Collaborative Operation): A situation where a specially designed robotic system works alongside a human operator in the same workspace.
Collaborative robots, or cobots, interact closely with humans in shared workspaces. Compared to traditional industrial robots, they are much safer and no longer require protective fencing when they meet certain safety standards.
Cobots are known for their high safety, ease of use, simple maintenance, and flexible deployment. They are widely used in machine tending, lab automation, polishing, palletizing, and assembly. In industries like automotive and electronics, cobots also play a key role. For example, they can accurately assemble LED light strips and assist human operators with screwdriving tasks, greatly improving productivity and reducing costs.
Ⅱ. Comparison Between Collaborative Robots and Traditional Industrial Robots
| Item | Collaborative Robots | Traditional Industrial Robots |
| Load Capacity & Adaptability | To ensure safety during human-robot collaboration, load capacity is generally limited. Typically under 20kg. The highest-capacity model, FANUC, can reach 35kg. | Load capacity ranges from a few kilograms to several hundred kilograms, up to 1 ton. |
| Precision | Generally lower than that of traditional industrial robots | High precision, with repeatability up to ±0.01 mm |
| Maximum Operating Speed | Generally less than 1,000 mm/s | Can exceed 2,000 mm/s |
| Simulation & Programming | Some brands support 3D simulation but may not support RobCAD or Process Simulate; usually use their own simulation software | Supports simulation and offline programming with tools like RobCAD and Process Simulate |
| Programming Interface & Language | Equipped with graphical or teach pendant-based programming; commonly use visual, flowchart, or scripting languages; flexible for mimicking human motion | Uses standardized languages; typically requires integration with external control systems; complex command structure |
| Safety | Designed to work with humans; built-in sensors stop the robot upon collision for safety | Requires safety fences, laser scanners, and other external safety measures; not designed to share workspace with humans |
| Communication Interface | Most models have built-in support for common protocols or support Profinet/Modbus, etc. | Communication typically requires PLC or middleware; supported protocols depend on model |
| Application Scenarios | Mainly used for tasks involving human collaboration, in confined spaces; flexible and diverse task types | Suitable for repetitive, hazardous, or space-constrained industrial tasks |
Ⅲ. Application scenarios of collaborative robots
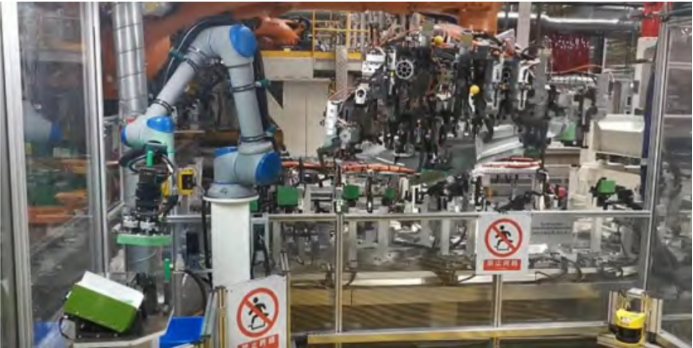
1.Application examples of collaborative robots in body shops
The application of collaborative robots in body shops mainly includes processes such as upper and lower parts, gluing, and screwing. In addition, they can also be integrated or connected to external vision systems.
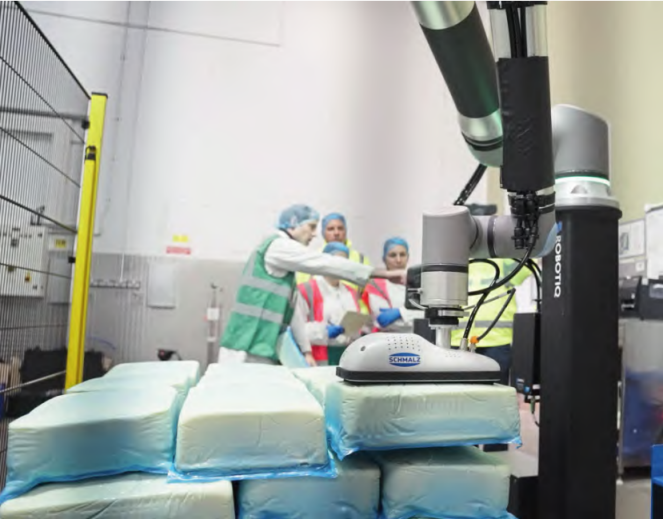
2.Palletizing and depalletizing with collaborative robots in the food industry
In food processing workshops, collaborative robots are lighter, easier to program, and more space-saving than traditional robots. Different models can handle a wide range of tasks—from picking up small, lightweight items to lifting large, heavy goods. They help reduce the physical burden on workers by taking over repetitive and tedious logistics tasks, such as faster palletizing and depalletizing.
Once a proper risk assessment is completed, cobots can work directly alongside human operators without the need for safety fences, significantly improving logistics efficiency at the end of the production line.

WEC-E20M Cobot – QUZHOU BOXIN TECHNOLOGY
WEC-E12M Cobot – QUZHOU BOXIN TECHNOLOGY
